Funtional Nanostructures
Researchers in the area of nanostructured materials optimize the development of these materials as oxide and noble metals, which when light is applied causes or facilitates chemical reactions capable of decompose contaminants, inhibit bacteria growth or even generate hydrogen (which is considered the future fuel).
This is what is known as the photocatalytic process, that is, the material response when it is illuminated. Actually, the challenge is to employ solar light or conventional illumination (fluorescent) with the purpose to take the most of them and get the same result. In this topic the works on research lines focused on finding materials and production methods that are more economical, efficient and easier to implement in industry.
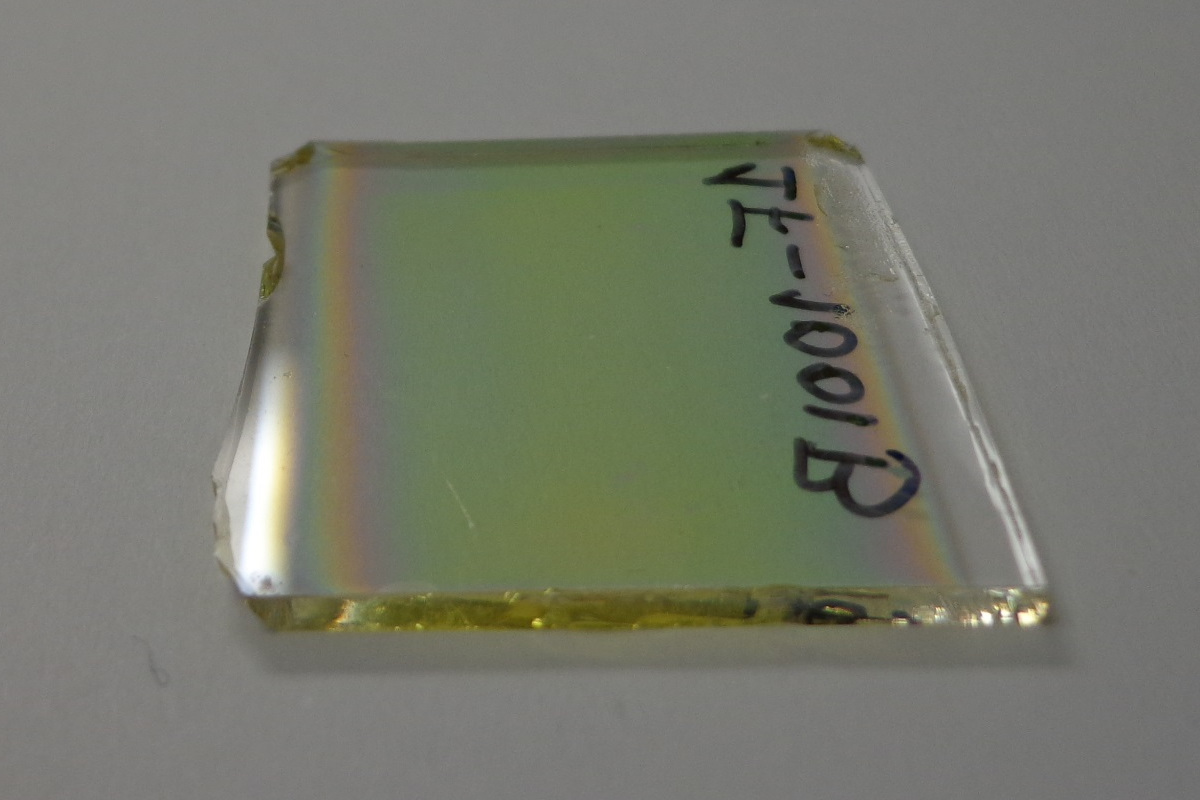
One technique developed in CIMAV uses salts to create nanomaterials, based on oxide and noble metals, with different structures like nanoparticles, nanorods, nano-threads or coatings.
Nanostructured materials have been deposited on ceramic, glass or metal and it is possible to include these materials on floors or walls. The substrate where these materials can be deposited could be flat (commercial ceramic, glass films) or on the inside or outside of tubes.
The innovation of this research is that scientists are studying nanostructures based on zinc oxide nanorods for organic matter degradation or hydrogen generation. The material can be implemented as antibacterial materials in hospitals, food production factories or public toilet, places where hygiene is essential and it would be possible to eliminate up to 90% bacteria in high risk places. As well, results can be, for example, implemented in water treatment plants.
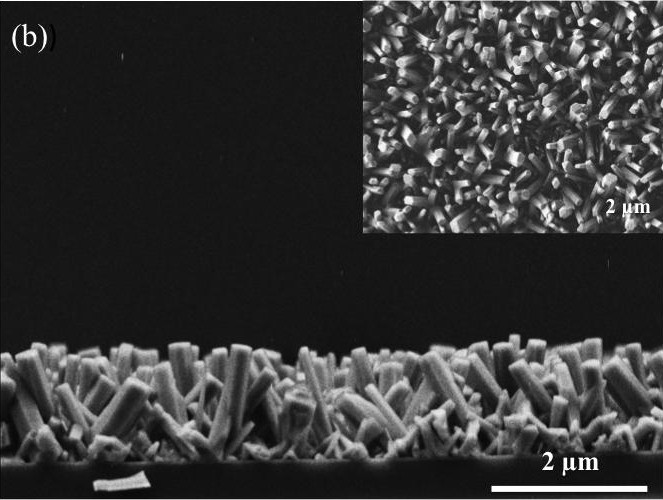
Thin films of Zinc oxide nanorods deposited on glass.
Zinc oxide nanorods are used to clean contaminated water, the system consists to place the thin film with nanorods inside of a transparent tube that allows solar light to have contact with the coating, where water goes through in stirring state. When solar light goes into the tube the physical-chemical process of the thin film is activated causing organic matter degradation. With this method is possible to clean up to 90-95% contaminated water at laboratory level.
This research group has been working on projects of technological development in collaboration with companies specialized in glass and ceramic with the purpose of improve their products for some of their applications like, for example, solar control or wear resistance.
It group had been developed nanostructured materials: resistant coatings, transparent conductive, optical coatings and materials for adsorption of heavy metals with the purpose to offer every client needs, and the develop of these materials at industrial level. Specialists seek to work primarily with materials that abound in nature, non-toxic, that can be developed with low cost techniques and that can be implemented in the industry. The studies had been generated national and international patents and articles published in high impact factor indexed scientific journals.
- Synthesis, microstructural characterization and properties of nanostructured materials base oxide and noble metals.
- Monolayer or multilayers, doped or compound.
- Solid or mesoporous nanoparticles, doped or compound.
- Nanorods, solids or core-shell, doped or compound.
- Carbon nanotubes and graphene.
- Functional nanostructured materials applications.
- Photocatalysis for environmental remediation or hydrogen generation.
- Chemical or mechanical resistant coatings.
- Transparent conductive materials.
- Optical coatings to filter ultraviolet light, visible or infrared.
- Heavy metals and other aqueous contaminant adsorption.
- Development of optoelectronic devices.
- Electron microscopy applications.

